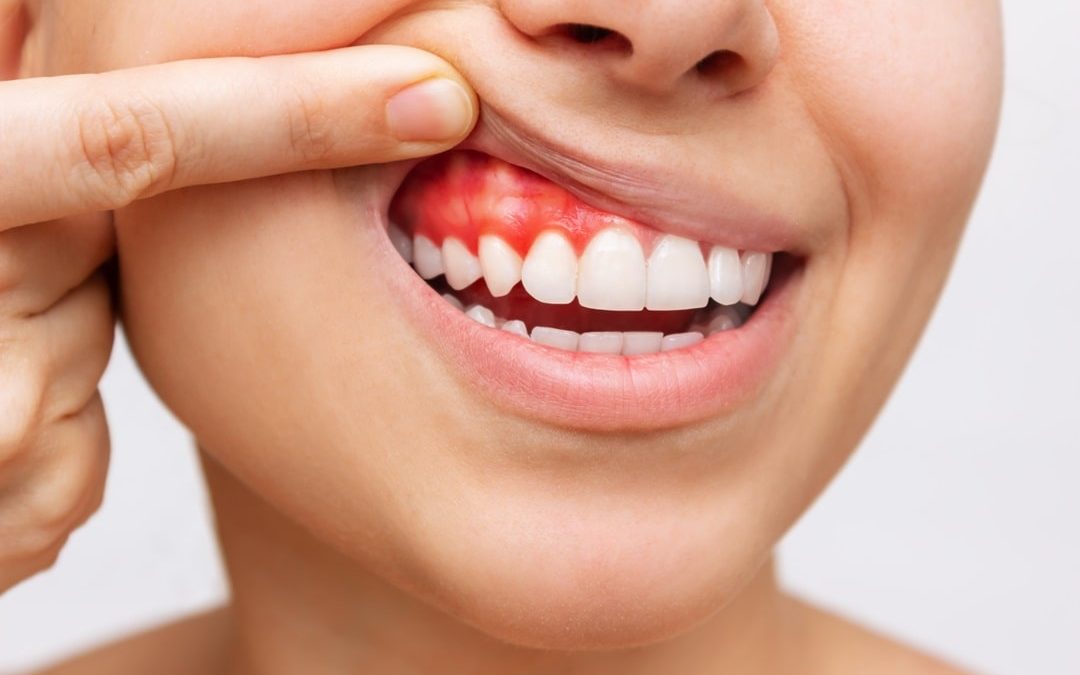
At SJD Dentists, we have developed a brief guide to gingivitis to explain everything about this periodontal disease, its symptoms and causes, as well as the importance of treating it correctly by periodontal specialists.
In this article, we will discuss in detail what gingivitis is, the main causes that lead to it, the most common symptoms, the diagnostic and treatment methods available, and the best practices to prevent it and maintain optimal oral health.
What is gingivitis and why is it important to treat it?
Gingivitis is an inflammation of the gums caused primarily by bacterial plaque buildup on the teeth. This condition, if not properly treated, can progress to periodontitis, a more serious disease that affects the bone supporting the teeth and can lead to tooth loss.
Symptoms include red and swollen gums, bleeding when brushing, bad breath and tooth sensitivity. These symptoms are often painless, which can lead to gingivitis going unnoticed until it becomes more severe.
Diagnosis of gingivitis is made by a complete dental evaluation, including a physical examination of the gums and x-rays to assess the health of the underlying bone. Treatment usually involves professional teeth cleaning to remove accumulated plaque and tartar, followed by instruction on proper oral hygiene techniques.
To prevent gingivitis you should maintain proper oral hygiene, brush your teeth at least twice a day, floss daily and visit the dentist regularly for dental cleanings and check-ups. Maintaining a balanced diet and avoiding smoking contribute to good gum health.
Main causes of gingivitis
Gingivitis develops mainly due to the accumulation of bacterial plaque on the teeth. Plaque is a film that constantly forms on the teeth and gums. If not properly removed by brushing and flossing, it can harden into tartar, which can only be removed by professional teeth cleaning.
Poor oral hygiene is one of the main causes of gingivitis. Smoking is another cause, as smokers are more likely to develop gum disease because smoking reduces the ability of the gums to heal.
Hormonal changes, such as puberty, pregnancy or menopause, can influence and make the gums more sensitive and vulnerable to gingivitis. Also, diseases that affect the immune system, such as diabetes, can increase the risk of gum infections.
In addition, some medications can influence the development of gingivitis, as can a diet low in essential nutrients such as vitamin C, which can also weaken the immune system and gums, making them more susceptible to inflammation.
Finally, there are genetic factors that can play an important role. A predisposition to develop gum disease can be hereditary. Remember, it is important to identify risk factors to prevent gingivitis and maintain optimal oral health.
Symptoms of gingivitis
Gingivitis can be a silent condition, as its initial symptoms are often mild and may go unnoticed. However, recognizing these early signs helps prevent progression to more serious disease such as periodontitis.
One of the most common symptoms of gingivitis is inflammation of the gums. The gums may appear red, swollen and tender to the touch. Bleeding when brushing or flossing is also common, a clear sign that the gums are irritated. In addition, you may experience persistent bad breath, known as halitosis, which does not go away despite good oral hygiene.
Another symptom is receding gums, where the gums pull away from the teeth, making the teeth appear longer. This can be a sign that gingivitis is progressing and causing damage to the supporting structures of the teeth. Tooth sensitivity may also increase, especially when consuming cold, hot or sweet foods and beverages.
At SJD Dentists, we recommend a complete dental evaluation if you notice any of these signs.
Diagnosing Gingivitis
Early diagnosis of gingivitis is important to prevent its progression and other serious complications. At SJD Dentists, we perform a complete dental evaluation to detect signs of gingivitis and determine the best treatment plan.
The first stage of diagnosis involves a detailed review of your medical history to identify any risk factors that may contribute to gingivitis, such as underlying medical conditions, medications or habits.
During the physical exam, our dentist will inspect your gums for signs of inflammation, redness, bleeding and sensitivity. We will use a periodontal probe, a special tool that measures the depth of the spaces (pockets) between your teeth and gums.
We use computed tomography (dental CT) scans to evaluate the health of the bones that support the teeth. This advanced imaging method allows us to accurately detect bone loss associated with periodontal disease to determine the condition and plan appropriate treatment.
Accurate diagnosis of gingivitis is key to initiating early and effective treatment, avoiding complications and keeping your gums and teeth healthy.
Treatment of gingivitis
The first step in treatment is a professional dental cleaning, which removes plaque and tartar buildup on the teeth and under the gums. This procedure, known as dental prophylaxis, helps reduce inflammation and promotes healing of the gums.
In more severe cases, scaling and root planing may be necessary. This procedure cleans the roots of the teeth to remove the bacteria and tartar that are causing the inflammation.
At SJD Dentists, we teach our patients effective brushing and flossing techniques to ensure proper cleaning of the teeth. In addition, regular dental visits are important to monitor the health of your gums and prevent the recurrence of gingivitis.
Preventing gingivitis
Preventing gingivitis is key to maintaining good oral health and avoiding major complications. To maintain healthy gums, brush your teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste, floss or use interdental brushes daily, and use a mouthwash.
Remember to have regular dental check-ups and professional cleanings to remove plaque and tartar that brushing cannot remove.
A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals, especially vitamin C and calcium, strengthens gums and teeth. Avoiding tobacco and limiting consumption of sugary foods and beverages also helps prevent plaque buildup.
Finally, be aware of any changes in the health of your gums, such as redness, swelling or bleeding, and seek dental care immediately if you notice these symptoms.
Complications of gingivitis
If not treated properly, gingivitis can lead to serious complications that affect more than just your oral health. The most common complication is periodontitis, which affects the supporting structures of the teeth, including the bones, and can cause tooth loss.
Chronic gum inflammation can also have other repercussions. Studies have linked periodontal disease to an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, such as heart attacks and strokes, and to complications in people with diabetes, making it difficult to control blood sugar levels.
Another possible complication is the development of periodontal abscesses, painful gum infections that cause swelling, severe pain and pus, and require immediate medical attention to prevent the spread of infection.
Gingivitis can also affect quality of life, causing persistent bad breath and painful or bleeding gums, which can make eating, drinking and talking uncomfortable. It is crucial to treat gingivitis in its early stages to avoid these complications.
Conclusion
Gingivitis is a treatable and preventable condition that, if addressed early, can prevent serious complications such as periodontitis. At SJD Dentists, we have specialists in periodontics to maintain optimal oral health and help you prevent and treat gingivitis in our dental clinics in San Cristobal de La Laguna and Las Chafiras.
Remember to maintain a proper oral hygiene routine, make regular dental visits and adopt healthy lifestyle habits are essential to preserve the health of your gums. If you are experiencing symptoms of gingivitis, do not hesitate to contact us for a personalized evaluation and treatment.


